If you’re trying to pick the Best ai workflow automation tools for your business, agency, or personal productivity stack, this guide is written for you. I’m Saas Guru, and over the past few years I’ve built and delivered dozens of AI-driven automations and agents for clients and internal teams.
In this long-form breakdown I’ll walk you through the practical differences between automations and agents, explain inputs and outputs, give a tool-by-tool analysis of nine platforms I use and evaluate, and finish with clear recommendations for different personae — business owners, agency founders, individual builders, and job seekers.
Throughout this post you’ll read candid pros and cons, screenshots pulled at relevant points in the demo, and real-life scenarios showing how each platform performs.
My objective is simple: help you pick from the Best ai workflow automation tools without getting stuck in analysis paralysis so you can ship production-ready automations fast.
Ai For Workflow Automation – Table of Contents
- How to read this guide
- Why the tool you choose matters (and why it often doesn’t)
- Quick primer: automations vs agents
- Inputs, outputs, and interfaces
- How I evaluated the Best ai workflow automation tools
- Tool reviews: 9 Ai Workflow Automation Tools
- Comparisons and how to choose
- Recommendations by persona
- Implementation checklist: from idea to production
- Common architectural patterns and examples
- Cost, risk, and long-term maintenance
- FAQ — Practical answers to common questions
- Final recommendations — the shortlist
- Closing thoughts
- FAQ — quick recap
How to read this guide
This is structured in three parts: a short conceptual primer (what is an automation, what is an agent, inputs/outputs and interfaces), an in-depth tool-by-tool review of nine platforms, and a practical recommendations section that tells you which platform to choose depending on your needs. I include screenshots at the exact moments in my demos that illustrate the point I’m making — you’ll find them interspersed, not at the end.
Because people keep asking, I’ll say it up front: you can build almost anything with almost any of these tools. The objective here is to help you decide quickly which platform fits your constraints — team skills, budget, need for self-hosting, and long-term maintenance.
Why the tool you choose matters (and why it often doesn’t)
There are two reasons the tool matters:
- Company backing and longevity: If you’re a business implementing automations that must run reliably for years, you want a platform with stable funding, active development, and community support. That matters for security, compliance, integrations, and hiring talent who know the tool.
- Operational fit: Different tools expose different export options, front-end interfaces, and templating systems. If you want a polished chat interface or a multi-step email automation engine, some platforms will get you there faster with fewer hacks.
And why the tool sometimes doesn’t matter:
- All modern platforms are converging. They all offer triggers, LLM steps, knowledge-base integrations, and ways to export an agent as a chat widget or API. If you can code or hire a developer, you can make almost any platform do what you need.
That said, the decision should be pragmatic: first understand what you need to deliver and pick the Best ai workflow automation tools that minimize friction for that goal.
Quick primer: Automations vs Agents
People use these words interchangeably, and that causes confusion. Here’s how I explain it to clients:
- Automations — processes that run in the background triggered by events (email received, cron schedule, webhook). They typically don’t require user input once configured. Example: an invoice processing pipeline that extracts data from emails and updates your accounting system.
- Agents — workflows that require an input (text, file, voice) and usually present a visual or conversational interface (chatbot, web form). Agents can also run autonomously, but they are designed around an interactive experience. Example: a prospect research agent you chat with to draft outreach sequences.
Understanding that difference helps you choose between back-end-first platforms (great for robust automations) and front-end-first platforms (better for conversational agents and chat interfaces).
Inputs, outputs, and interfaces
When designing an AI workflow automation you always think in terms of inputs and outputs:
- Inputs — manual (text, files, voice messages, forms) or automated (webhooks, email triggers, scheduled jobs).
- Processing — model steps, vector store lookups, tool calls, conditional branching.
- Outputs — backend side effects (API calls, database updates, emails) or visual outputs (chat messages, files, images, dashboards).
Most platforms give you a canvas to wire nodes representing those steps. The final piece is the interface: sometimes you will use the platform’s native widget or export a link; other times you’ll build a separate front end (chat widget, messenger channel, Airtable interface) and point it at the workflow’s API.
How I evaluated the Best ai workflow automation tools
Practical filters I use:
- Funding and roadmap — will the vendor be around in two to three years?
- Export options — can I embed the agent as a widget, export to Slack, or access via API?
- Integrations — does it connect to databases, storage, email providers, CRMs?
- Templates and community — how much documentation, templates, and third-party content exist?
- Developer friendliness — is there an SDK, custom API blocks, or JavaScript functions?
Now — let’s go tool-by-tool. Each section covers the core pitch, who should use it, strengths, weaknesses, and brief real-life use examples.
Tool reviews: 9 Top Ai Workflow Automation Tools
1) Stack AI

Positioning: Enterprise-focused AI agents builder. I find their marketing calls it Enterprise, but in practice Stack can be used by a wide range of companies.
About Company: Founded recently, seed funding (~$3M), price tiers that skew higher (example $200/mo tier). The team is small, but Stack focuses on export options and connectors.
- Clean visual canvas that feels familiar if you like node-based builders.
- Multiple export options including Chrome extension, web chat, API, Slack app — excellent for prototyping and delivering to clients quickly.
- Good template resources for common agent patterns (document comparison, chat assistants).
Limitations:
- Smaller company, less mass adoption, fewer community tutorials than more established players.
- Not the largest set of integrations by default; complex integrations may still require a developer workaround.
Real-life example: I used Stack for a quick document comparison agent prototype. The canvas allowed me to upload documents, pass them through a vector store node, and call an LLM node to return comparison notes. Exported it as a form for the client to test, copied the output into Gmail drafts for manual review.
Best for: Agencies who value a sexy export story for prototypes and teams that want a visually neat canvas with multiple embed options.
2) Dify
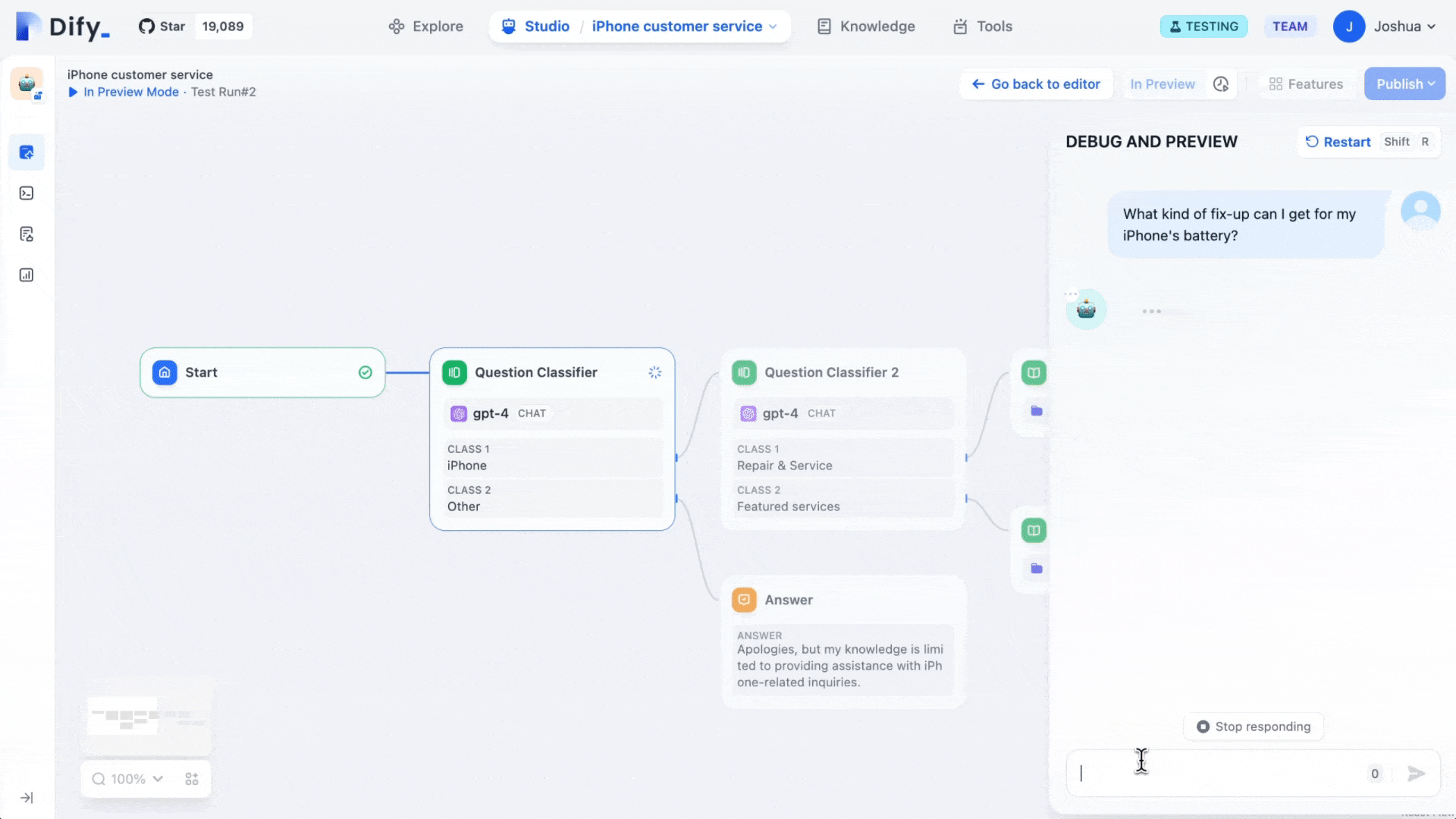
Dify is an open-source aagent builder that made waves because it can be self-hosted. Private company, no major VC rounds. If you want to self-host and control everything, it’s attractive.
- Self-hostable, flexible, supports knowledge base uploads, Notion sync, website scraping.
- Standard canvas with classifiers, LLM steps, and actions — essentially the same primitives as other platforms.
- Good for experimenters who want full control without vendor lock-in.
Limitations:
- Not a major amount of tutorials or community content compared to bigger platforms.
- Smaller company footprint — limited investment compared to funded startups.
Real-life scenario: Great if you want to self-host a document Q&A agent that crawls your internal site and serves answers to staff via a Slack integration you control.
Best for: Technical teams and self-hosting enthusiasts who want to own their infra and avoid cloud vendor lock-in.
3) Lindy
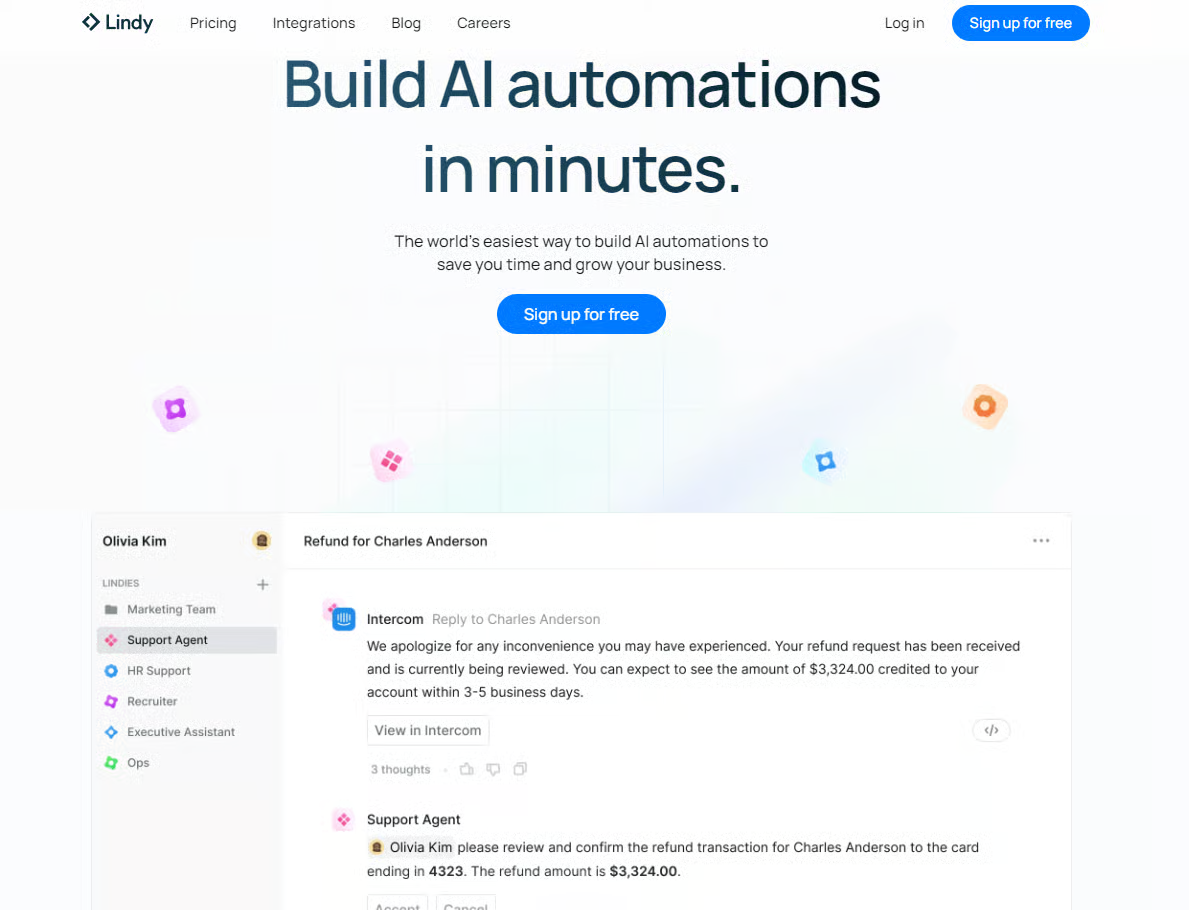
Lindy has been one of the fastest-growing entrants. Founded ~2023 with large funding rounds (I found reported rounds around tens of millions). The product strongly leans into email automation and flow-like sequencing.
Why use Lindy:
- Sequential flow builder that feels like email automation tools (easy for marketers and operations folks).
- Native smart conditional logic — you can build waiting steps (wait for an email reply or a trigger) without architecting separate automations.
- Great for automating inbox workflows: triage, auto-responses, draft generation based on your knowledge base.
Limitations:
- Newer market entrant but well funded — which is a plus for longevity, but there’s still limited community content relative to older tools.
- Some advanced customizations may be tricky for external developers who don’t use Lindy daily.
Real-life example: Use Lindy to automate a sales outreach engine that sends a prospecting email, waits three days for reply, checks if a reply exists using the knowledge base, and branches into follow-up or escalate-to-human flows. The wait-for-reply primitive makes this smooth.
Best for: Business teams that need realistic email automation with conditional waits and readable sequential flows.
4) VectorShift
VectorShift is developer-forward — think pipelines plus a Python SDK. It’s particularly strong if you want to mix multiple LLM providers and run complex transformations.
Company snapshot: Seed funding (~$3M), YC background. Strong integrations and flexibility.
- Pipeline concept that’s ideal for processing data at scale (bulk jobs, transformations).
- Support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Hugging Face, etc. — great if you want to hedge across models.
- Forms, portals, and built-in integrations make prototyping fast when you need external input.
Limitations:
- Developer oriented — non-technical users can be intimidated by SDK language and deployment-oriented options.
- Smaller team / less mass adoption than the largest players — fewer community resources.
Real-life scenario: Use VectorShift to analyze Notion data, run a GPT-4 report generator, and post results into Slack. Use Python transforms to normalize inputs before model calls.
Best for: Teams that want flexible multi-LLM workflows and are comfortable with developer tooling.
5) Relevance AI
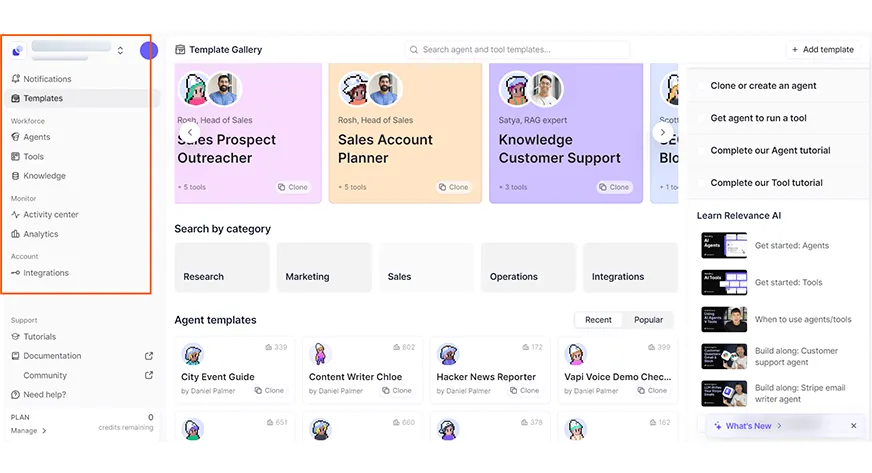
Relevance emphasizes agent-first design. They give you building blocks (tools) you can reference in your agent instructions and let you compose sub-agents. Relevance has a strong template library and a founder that’s active in the community.
Company snapshot: More mature than some newcomers, reported funding in the low-to-mid tens of millions and a steady growth trajectory.
Why use Relevance:
- Agent-structured design: name your agent, give core instructions, attach tools like Google Search or Slack. This maps well to real-world tasks.
- Templates that are useful, not just toy examples — you can copy and adapt agents for sales research, HR workflows, and content generation.
- Ability to embed references to tools reduces hallucinations by explicitly informing the agent what to call and how.
Limitations:
- Less visual than some canvases — if you are a heavy visual learner you might find it less intuitive at first.
- We haven’t shipped a final client project fully on Relevance in our agency yet — we used it for prototypes extensively.
Real-life example: Build a prospecting agent that scrapes company websites, drafts targeted outreach, and sequences follow-ups. The agent can call a Google Search tool, a LinkedIn scraping tool, and a send-email tool as separate primitives.
Best for: Builders who prefer an agent-first mental model and need pre-built, useful templates for business tasks.
6) Zapier

Zapier is the legacy automation player that many organizations already know. Post-AI world, Zapier added AI features and a step-by-step builder. It’s robust, familiar, and backed by an established organization.
- Unmatched catalog of integrations and long-term stability.
- Lots of tutorials and an ecosystem of Zap-based solutions.
Limitations:
- UI feels older and more linear — not a dynamic canvas like Node-based builders.
- Pricing for heavy users can get expensive.
- Not positioned as an AI-native platform; its AI features are additions rather than central constructs.
Real-life scenario: Zapier remains useful when you need straightforward app-to-app automation and there’s no need for advanced LLM-driven logic. If your company already has many zaps, extending them with AI steps can be pragmatic.
Best for: Organizations that value stability and integration breadth more than AI-first features.
7) n8n
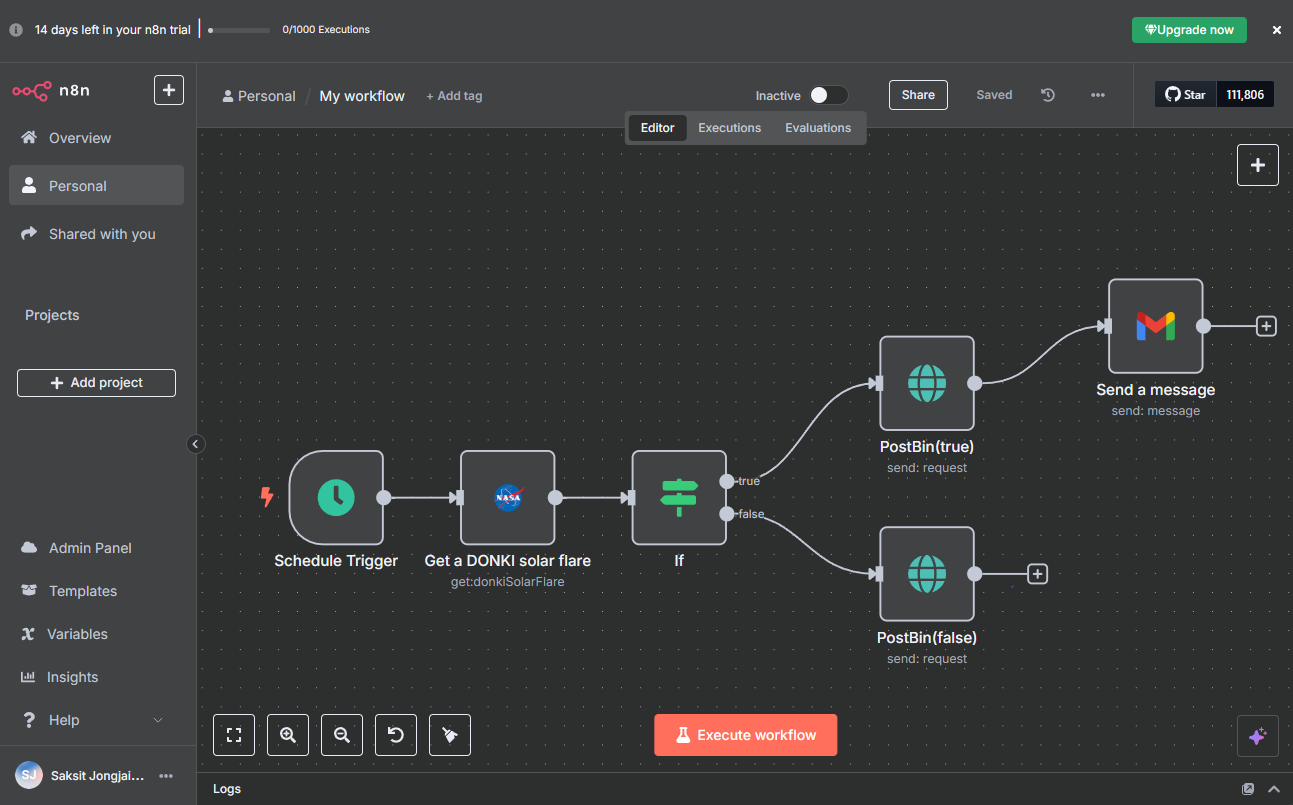
n8n is the self-hosting friendly automation tool that’s been gaining viral momentum. It’s often compared to Make but positioned as developer-friendly visual automation that maps closely to code.
Why use n8n:
- Self-hosting capability for teams that need full control.
- Developer-friendly nodes that feel like a visual representation of code — great for complex data pipelines and complex DB integrations.
- Growing library of community tutorials and templates.
Limitations:
- Steeper learning curve for non-technical users.
- Installation/self-hosting overhead if you don’t want a managed option.
Real-life scenario: We used n8n for a client that required self-hosted automation due to compliance constraints. We delivered a full pipeline and trained the client to maintain it.
Best for: Enterprise teams or dev-heavy shops that require self-hosting and complex integrations.
8) Make (formerly Integromat)
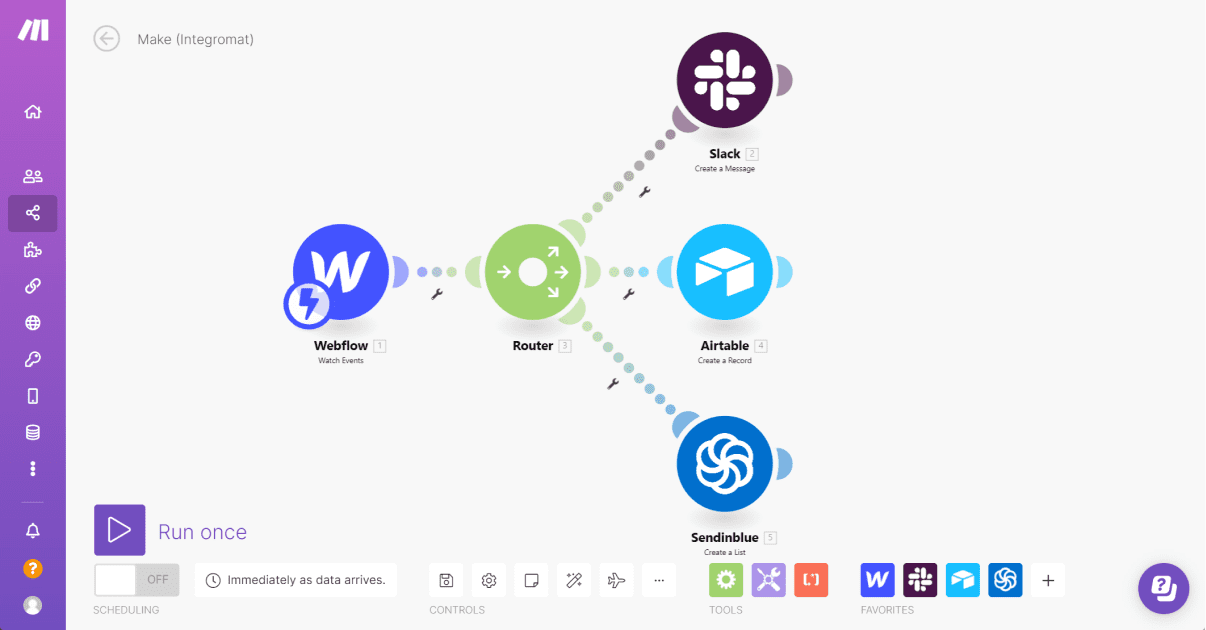
Make is the visual automation platform we often use at the agency. It’s flexible, widely adopted, and has an extensive module library.
Why use Make:
- Powerful visual builder with lots of modules and an approachable UI for non-developers.
- Large community, many templates, and generous built-in functions like iterators and aggregators.
- Simplifies complex automations without writing code — most missing integrations can be solved via HTTP requests or built-in SDKs.
Limitations:
- No native front-end chat interface — Make is back-end first (but you can pair it with front-end tools like ChatDash or Voiceflow).
- Some advanced transformations require familiarity with iterators, mappings, and basic JavaScript logic.
Real-life example: Building production-grade automations for client CRMs, email campaigns, and multi-step document processing. Make was perfect because the client expected maintainability and clear handoff to non-dev stakeholders.
Best for: Agencies and SMBs that want approachable but powerful back-end automation with great community support.
9) Voiceflow
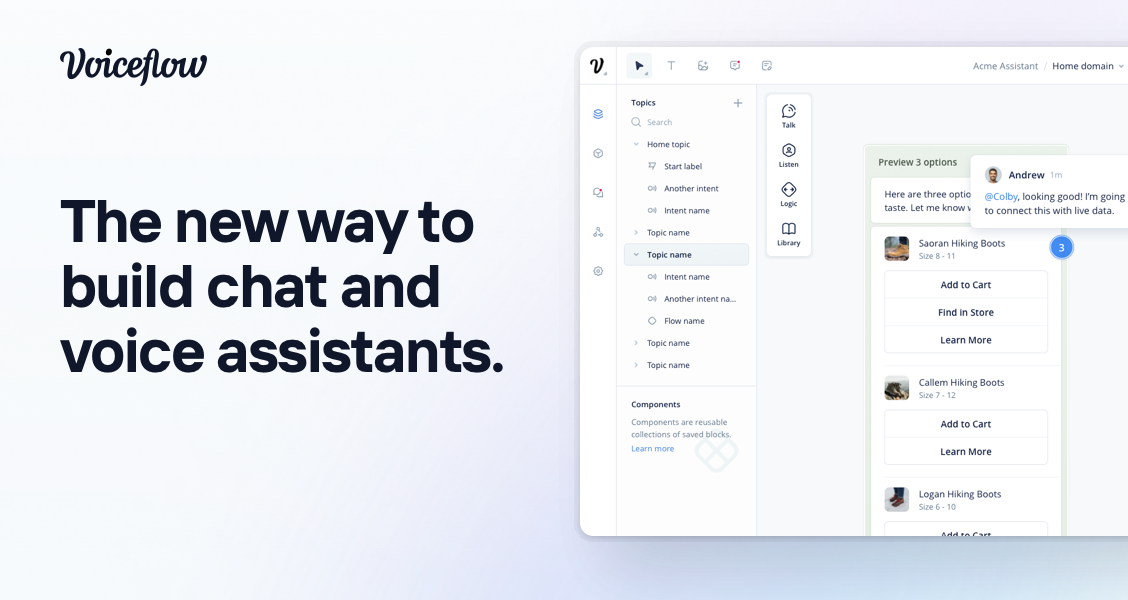
Voiceflow is my go-to for conversational, text-based agents. If your primary goal is a chat or voice interface with advanced dialog design and knowledge-base extraction, Voiceflow is the best choice in this list.
Why use Voiceflow:
- Exceptional conversational design tools and advanced knowledge-base handling.
- Functions marketplace (reusable blocks) and support for APIs make it easy to wire to your systems.
- Great for customer support agents, lead qualification bots, or any scenario requiring rich conversation flows and analytics.
Limitations:
- Export channels and integrations are less turnkey in some cases — you may need to build intermediate systems for WhatsApp, advanced CRM connect, or custom databases.
- Function marketplace isn’t yet as active as it could be; fewer community-shared functions than I’d like.
Real-life scenario: We built a sales support agent that asked discovery questions conversationally, wrote notes to Airtable, and surfaced dynamic suggestions to reps. Voiceflow’s conditional nodes, slots, and response design made this possible rapidly.
Best for: Text- and voice-conversational agents for customer-facing use cases and internal conversational workflows for sales/support teams.
Comparisons and how to choose
Let me get practical: here’s a quick decision heuristic I use when recommending the Best ai workflow automation tools to clients.
- If you want quick email automations and conditional wait states: Lindy — easiest entry for email-first workflows.
- If you want a polished conversational agent/web chat: Voiceflow — best conversational UX and analytics.
- If you need a back-end automations engine with broad adoption and easy handoff to a non-dev team: Make — best balance of power and learnability.
- If you must self-host for compliance: n8n or Dify — self-hosting friendly.
- If you want developer flexibility and multi-LLM support: VectorShift — pipelines + Python SDK.
- If you want an agent-first model and excellent templates: Relevance — lots of useful agent templates and a clear agent model.
- If you need to prototype fast with modern embed/export options: Stack AI — great export options and neat canvas for prototypes.
- If you want maximum integrations and corporate robustness: Zapier — proven, though not AI-first.
Recommendations by persona
Business owner (building for your company)
If you’re a business owner implementing automations that must be maintained long-term, I recommend choosing platforms with funding and community support. My three picks:
- Lindy — for email-first, flow-based automation that non-developers can manage.
- Make — for comprehensive back-end automations with a friendly UI and large community.
- Voiceflow — for conversational customer-facing agents where experience and analytics matter.
Why these? They balance ease-of-use with long-term viability and hiring pool availability. If you have strict hosting or compliance requirements, add n8n and Dify to the shortlist.
Agency or consultant (selling AI services)
For agencies that sell implementations and retainers I recommend mastering Make plus one conversation platform (Voiceflow) and getting comfortable with n8n for self-hosted clients. Mastering Make gives you the fastest time-to-delivery for most clients; Voiceflow covers the high-value chatbot work; n8n covers cases where clients insist on self-hosting.
Additionally, knowing VectorShift and Relevance as secondary tools is helpful: VectorShift for dev-heavy LLM projects, Relevance for agent-first offers you might resell or white-label.
Individual / productivity builder
If you’re automating personal workflows or building portfolio projects, pick platforms that reduce learning friction. Relevance and Lindy are approachable and let you iterate fast. Make is also great for hobbyists once you learn iterators and mappings.
Job seekers (automation engineer / consultant roles)
Look for job descriptions asking for Make or n8n experience. These two have large markets. Also learn JavaScript and APIs — they are essential when you need to write functions, transformations, or debug integrations. Add Voiceflow to your CV if you want roles focused on conversational design.
Implementation checklist: from idea to production
- Define the goal and measure: what to automate, and what KPIs will determine success?
- Map inputs and outputs: Identify triggers, expected outputs, and any external APIs or knowledge sources you’ll need.
- Choose the Best ai workflow automation tools that align with your constraints (budget, hosting, team skills).
- Prototype: build an MVP agent or automation and test with a closed group.
- Monitor and iterate: instrument logs, track model costs and accuracy, add rate limiting and human-in-the-loop where necessary.
- Plan for maintenance: decide who will update prompts, retrain vector indices, and maintain integrations.
Common architectural patterns and examples
Here are patterns I use repeatedly, and the Best ai workflow automation tools I pair with them:
- Document Q&A agent: Vector store (embedding + vector DB) -> LLM context -> agent interface. Tools: Stack, Relevance, Voiceflow.
- Sales outreach automation: Prospect scraping -> AI personalization -> email sequence with conditional waits. Tools: Lindy or Make + Lindy for email step.
- Invoice processing: Email trigger -> OCR/pdf parsing -> LLM extraction -> accounting API update. Tools: Make or n8n for reliable connector support.
- Conversational support bot: Knowledge base -> conversational design -> API calls to CRM -> human handoff. Tools: Voiceflow + Make/n8n for back-end connectors.
Cost, risk, and long-term maintenance
Costs are multi-dimensional: subscription fees, model API usage, data storage (vector DB), and engineering time. When evaluating the Best ai workflow automation tools, estimate the second-order costs: how will you update prompts? Who will keep knowledge bases fresh? How will you monitor hallucinations and escalate to humans?
Tip: start with a sandboxed prototype in the cheapest tier that allows you to measure the largest unknown (usually LLM cost or integration complexity). Then scale the service plan as usage grows.
FAQ — Practical answers to common questions
Q: What exactly is an AI workflow automation tool?
A: An AI workflow automation tool is software that lets you design and execute a sequence of tasks, often by connecting apps and invoking AI models, to automate repetitive or complex processes. It can automate triggers (like “email received”) and perform actions (send replies, update databases), and/or present agent interfaces (chat widgets, forms) for interactive experiences. The Best ai workflow automation tools integrate model calls, vector searches, and tool-specific connectors into a single builder.
Q: How do I choose between an agent-first tool and an automation-first tool?
A: Start with the primary interaction model. If human users need a conversational interface or a chat-first experience, prioritize Voiceflow or Relevance. If your workflows are backend automations triggered by events, Make or n8n will be better. If you need both, choose a tool that supports APIs and embed/export options so you can pair front-end and back-end tools.
Q: Do I need to know programming to use these tools?
A: Not strictly. Many platforms are no-code and let non-developers build complex automations. However, a basic understanding of JavaScript, APIs, and JSON significantly expands what you can build — especially around iterators, data mapping, and custom HTTP requests. For agency work and professional-grade projects, JavaScript and API fluency is almost always necessary.
Q: What’s the best choice for companies that must self-host?
A: n8n and Dify are the most self-host friendly. They let you run automation engines on-prem or in your cloud account. This is important for compliance, security, and cost control in larger organizations.
Q: Can these tools prevent hallucinations?
A: No tool can eliminate hallucinations entirely, but some practices and tool features reduce them: using reliable tool references (telling agents which tool to call for a specific action), including structured knowledge base context (vector retrieval + citations), and instrumenting audits and human-in-the-loop checks. Relevance’s explicit tool references and Voiceflow’s ability to design conditional steps help reduce hallucinations in practice.
Q: If I’m building an agency, which stack should I master?
A: Start with Make for general automations and Voiceflow for chat agents. Add n8n as a differential selling point for self-hosting clients. Learn how to pair Make with Voiceflow when clients need both strong back-end automation and conversational front ends. Become comfortable with APIs and JavaScript — these are your multiplier skills.
Final recommendations — the shortlist
After testing and shipping projects across platforms, here are the concise recommendations I give clients asking for the Best ai workflow automation tools:
- Businesses (internal & production): Lindy + Make + Voiceflow (choose Lindy for email flows, Make for automations, Voiceflow for chat agents).
- Agencies: Master Make and Voiceflow, know n8n for self-host cases, and add VectorShift or Relevance for complex agent builds or multi-LLM strategies.
- Individuals: Relevance (lower friction, great templates) or Lindy for email automation experiments.
- Job seekers: Learn Make and n8n; add Voiceflow to your portfolio for conversational roles.
Remember: the Best ai workflow automation tools are the ones that let you ship value fast and maintain it reliably. Choose a platform that matches your team’s skill set, your project’s complexity, and your long-term maintenance expectations.
Closing thoughts
There’s no single “perfect” platform. These nine tools I reviewed — Stack AI, Dify, Lindy, VectorShift, Relevance, Zapier, n8n, Make, and Voiceflow — each have strengths that make them the Best ai workflow automation tools depending on your use case.
If you’re starting today and want the fastest path to results, pick one, ship, measure, and iterate. The real competitive advantage is in execution, not the logo on your automation canvas.
If you want practical help taking a prototype to production or packaging agents you can resell, I run training and templates to help agencies and consultants sign their first high-ticket automation clients.
But the most important step is the first one: decide your desired outcome, pick the tool that maps to it, and build something small that delivers measurable impact.
FAQ — quick recap
- Which single workflow automation tool should beginners try?
- Relevance or Lindy — both have lower learning friction and useful templates.
- Which Ai tool is best for conversational agents?
- Voiceflow — advanced dialog design and analytics.
- Which Ai tool is best for back-end workflow automations?
- Make — balance of power and community; n8n for self-hosting.
- Which Ai aAutomation tool is best if I want developer flexibility and multi-LLM support?
- VectorShift.
Thanks for reading. If you have a specific use case — internal knowledge agents, outbound sequences, invoice processing, or FAQ bots — post your scenario and I’ll advise which of the Best ai workflow automation tools will get you to a production outcome fastest.





